Sustainable and actionable: An ESG study of climate and social challenge for Asia
Along with its wealth, Asia’s climate risks have been rising. Low-lying coastal cities are particularly vulnerable to climate change and regional population and economic centres—such as Bangkok, Ho Chi Minh City, Manila and Shanghai—sit upon that precipice. Yet in terms of green fixed income, Asia faces another risk: lack of issuance and uptake.
Related content

Data drives ESG investing—but too much data inspires greenwashing
Greenwashing—falsely attracting capital by claiming it will be used for sustainable projects—is the “fake news” of investing. The term has roots in the 1980s when it was aimed at big corporations that made symbolic “green” gestures but were nonetheless culpable for net contributions to pollution, or what we today call “climate change” (a greenwashed term itself that displaced “global warming”).
But with the growth of environmental, social and governance (ESG) investing, which now accounts for about 20% of global assets under management (AUM),1 the stakes are much higher.
“Greenwashing is a big issue,” says Remy Briand, global head of ESG products at MSCI. The finance firm is a major provider of investment indices and data, much of which is ESG focused. “The way to resolve this is through transparency on dedicated use of proceeds and robust third-party validation of that use.”
The mention of “transparency”, however, raises the question of how it’s to be achieved. The old answer might have been “more data”. But one problem the financial world faces is a lack of a global ESG taxonomy which means there is no data “gold standard”. Information can therefore be highly inconsistent, making comparison of companies and projects difficult. In turn, that deters investors and helps greenwashers. Many of Asia’s largest investors—the asset owners—such as the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, the Hong Kong Monetary Authority and Ping An Insurance, China’s biggest insurer, share this view (their perspectives are shared in The Economist Intelligence Unit report, Sustainable and actionable: An ESG study of climate and social challenge for Asia).
A question investors are starting to ask of ESG is “What’s so green about it?”
About 600 organisations claim to answer that question, Mr Briand comments. The multitude of data then can muddy the waters more than it clarifies. These entities are all trying to convince investors that they have built the best ratings mousetrap and go on to ask listed and private companies for widely diverging ESG data, exhausting both corporate patience and resources. Such an over-proliferation “can be an excuse to do nothing,” Mr Briand asserts.
With no overarching taxonomy to define “green” and an excess of providers and methodologies, the space between problems and solutions only gets wider. So the answer can’t be “more data”.
“The important point is that investors need to be explicit about the problem they are trying to solve,” says Mr Briand. For instance, a listed fishing company that operates unsustainably will see its supply collapse—and its business with it. Translating the scenario into conventional financial metrics such as default risk is called “materiality” and is seen by many investors as a more applicable approach.
Focusing on metrics can do more to influence ESG investment strategies and outcomes than the heavy data burden associated with proving ESG credentials. A shift in focus should help to address issues such as cost of capital which has hampered green bond uptake. It’s not that investors shun the green aspect, but when issuers have to jump through too many hoops to get a bond certified, they walk away. Bureaucracy comes at a cost and it’s a common complaint among issuers that they reap no reward for the extra effort of issuing a green-labelled bond. Again, the extra data leads to fewer green investment opportunities (but more greenwashing ones).
However, Mr Briand believes change may be on the way. He explains how MSCI has analysed issuers within its own green bond indices and found a difference between those with high green credentials and those with low. “Investors put a premium on those bonds issued by the former. So, regarding the question as to whether investors discriminate between the two, the answer is yes.” Higher demand, when seen as truly accomplishing a green goal, does translate into a lower cost of capital.
Having a grasp on materiality benefits investors because such company-level transparency can flag risks—from exposure to floods to regulatory action or labour disputes—that negatively impact value.
Data used in this way could overtake the need for green-labelled financial instruments and the related greenwashing potential. Greenwashing is akin to a cigarette manufacturer touting a one-off charitable donation to lung cancer research. It might look good in the data but we all know what the root cause is. Progress in leveraging capital against climate change depends on better linkage between green goals and quantifiable key performance indicators.
Investors need the ability to apply standardised data all the way through portfolios so that all AUM can be green, not just those with the right boxes ticked.
Special thanks to Remy Briand, global head of ESG products, MSCI for his insight and expertise on the topic.
For a deeper analysis on ESG, green credentials and greenwashing see Sustainable and actionable: An ESG study of climate and social challenge for Asia
1 US$17.5trn out of the US$79trn of total estimate from Boston Consulting Group and the US SIF Foundation, cited in the Financial Times, February 26th 2020. https://www.ft.com/content/e969217c-f001-11e9-a55a-30afa498db1b?segmentId=47561bcd-230d-6768-b4a1-deb6edc93a7b

Sustainable and actionable: A study of asset-owner priorities for ESG inves...
The world’s top 100 asset owners (AOs) represent about US$19trn in assets under management. The largest, and potentially most influential, proportion is in Asia—more than a third of the total. Out of the top 20 largest funds, three out of the first five and nearly half of the total are in Asia.
The Economist Intelligence Unit carried out interviews with some of Asia’s largest asset owner firms, development banks, sustainable investment organisations and influential industry advocates to determine how they saw the growth of environmental, social and governance (ESG) investing in Asia, as well as the AO role in it. In parallel, we review the latest research on ESG investing in the region to give an overview of sustainable investing in Asia. The main findings include:
There has been a significant change in the awareness, uptake and impact of ESG in Asia over the past three to five years. AOs are motivated by an increasing recognition that their investment decisions have material consequences for their environment and the lives of their beneficiaries. In terms of financial return, “governance” seems to be the most important ESG factor for most AOs, given its demonstrable link to optimising risk-adjusted returns. As in other regions, ESG investing began with a negative screening approach. While progress is accelerating, challenges remain.
The shifting landscape of global wealth: Future-proofing prosperity in a ti...
In some instances the impact of this shift will be shaped by local factors, such as demographic changes. In other instances this shift will reflect shared characteristics, as demonstrated by the greater popularity of overseas investing among younger high-net-worth individuals (HNWIs) brought up in an era of globalisation. Whatever the drivers, the landscape of wealth is changing—from local to global, and from one focused on returns to one founded on personal values.
Despite rising economic concerns and a tradition of investor home bias in large parts of the world, the new landscape of wealth appears less interested in borders. According to a survey commissioned by RBC Wealth Management and conducted by The Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU), younger HNWIs are substantially more enthusiastic about foreign investing. The U.S. is a particularly high-profile example of a country where a long-standing preference for investments in local markets appears set to be transformed.
Click the thumbnail below to download the global executive summary.
Read additional articles from The EIU with detail on the shifting landscape of global wealth in Asia, Canada, the U.S. and UK on RBC's website.
Data drives ESG investing—but too much data inspires greenwashing
Related content

Sustainable and actionable: An ESG study of climate and social challenge fo...
Along with its wealth, Asia’s climate risks have been rising. Low-lying coastal cities are particularly vulnerable to climate change and regional population and economic centres—such as Bangkok, Ho Chi Minh City, Manila and Shanghai—sit upon that precipice. Yet in terms of green fixed income, Asia faces another risk: lack of issuance and uptake.
Fixed-income plays a significant role in climate mitigation because its market is about 60% larger than its equity cousin which still attracts more media and investor attention. Global issuance of green fixed income has increased markedly since its inception, reaching US$350bn in 2019. Still, the amount is only about 5% of the global fixed income market and represents just over a tenth of what needs to be raised to meet Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in emerging markets alone.
Efforts to make Asia’s finance greener have marked a transformative effect on the relationship between companies and investors. Conversations about sustainability that were absent a decade ago are now happening and have been central to helping the region come so far in such a short time: Asia’s banks and corporates have gone from 1% of green issuance in 2013 to 45% in 2019.
Still, not all is rosy (or green) as many obstacles remain. Asia’s green fixed income originates from a narrow base. China is the dominant market regionally and credit quality is largely confined to supranational institutions and investment-grade issuers. That is not enough. Other markets, such as high-yield, assetbacked securities (ABS) and private debt are, at best, in infancy. Furthermore, developedmarket investors tend to underweight Asia.
Green fixed income data is also a persistent challenge. A profusion of providers use a wide range of methodologies, many of which can be opaque and defy comparison. Investors face difficulties in determining those which best suit their needs. The vast amount of data that issuers are required to provide can also be a deterrent to going green; or worse, it leads to “greenwashing”, a vexing problem of questionable categorisation globally. The emergence of more consistent taxonomies is helping, but the patchwork of approaches still forms a barrier. Market practitioners interviewed for this paper did find agreement on green fixed income limitations, but they also showed optimism that recent developments in debt-products indicate a positive direction, even if the needle measuring progress has yet to move as far as it should.
From consensus, the region’s green fixed income progress depends on the development of a consistent taxonomy—not just in Asia, but globally—as well as better linkage of Paris Agreement goals to quantifiable key performance indicators (KPIs). The result could create better incentives for issuers and asset owners alike.
Have green bonds—as the largest green fixed income competent—been enough? Despite the interviewees’ breadth of experience and varied professional functions, they are almost entirely synchronised in their response to this question: “no”.
So what’s next?

Sustainable and actionable: A study of asset-owner priorities for ESG inves...
The world’s top 100 asset owners (AOs) represent about US$19trn in assets under management. The largest, and potentially most influential, proportion is in Asia—more than a third of the total. Out of the top 20 largest funds, three out of the first five and nearly half of the total are in Asia.
The Economist Intelligence Unit carried out interviews with some of Asia’s largest asset owner firms, development banks, sustainable investment organisations and influential industry advocates to determine how they saw the growth of environmental, social and governance (ESG) investing in Asia, as well as the AO role in it. In parallel, we review the latest research on ESG investing in the region to give an overview of sustainable investing in Asia. The main findings include:
There has been a significant change in the awareness, uptake and impact of ESG in Asia over the past three to five years. AOs are motivated by an increasing recognition that their investment decisions have material consequences for their environment and the lives of their beneficiaries. In terms of financial return, “governance” seems to be the most important ESG factor for most AOs, given its demonstrable link to optimising risk-adjusted returns. As in other regions, ESG investing began with a negative screening approach. While progress is accelerating, challenges remain.
The shifting landscape of global wealth: Future-proofing prosperity in a ti...
In some instances the impact of this shift will be shaped by local factors, such as demographic changes. In other instances this shift will reflect shared characteristics, as demonstrated by the greater popularity of overseas investing among younger high-net-worth individuals (HNWIs) brought up in an era of globalisation. Whatever the drivers, the landscape of wealth is changing—from local to global, and from one focused on returns to one founded on personal values.
Despite rising economic concerns and a tradition of investor home bias in large parts of the world, the new landscape of wealth appears less interested in borders. According to a survey commissioned by RBC Wealth Management and conducted by The Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU), younger HNWIs are substantially more enthusiastic about foreign investing. The U.S. is a particularly high-profile example of a country where a long-standing preference for investments in local markets appears set to be transformed.
Click the thumbnail below to download the global executive summary.
Read additional articles from The EIU with detail on the shifting landscape of global wealth in Asia, Canada, the U.S. and UK on RBC's website.
Financing sustainability | Insights video
What is driving the strong demand for financing sustainability in Asia Pacific? How can companies increase supply and start to see the benefits of sustainable finance in the next three years? We interviewed Richard Brandweiner, CEO of Pendal Australia, and Sophia Cheng, CIO of Cathay Financial Holdings and chair of Asia Investor Group on Climate Change, to find out.
Related content

Financing sustainability: Asia Pacific embraces the ESG challenge
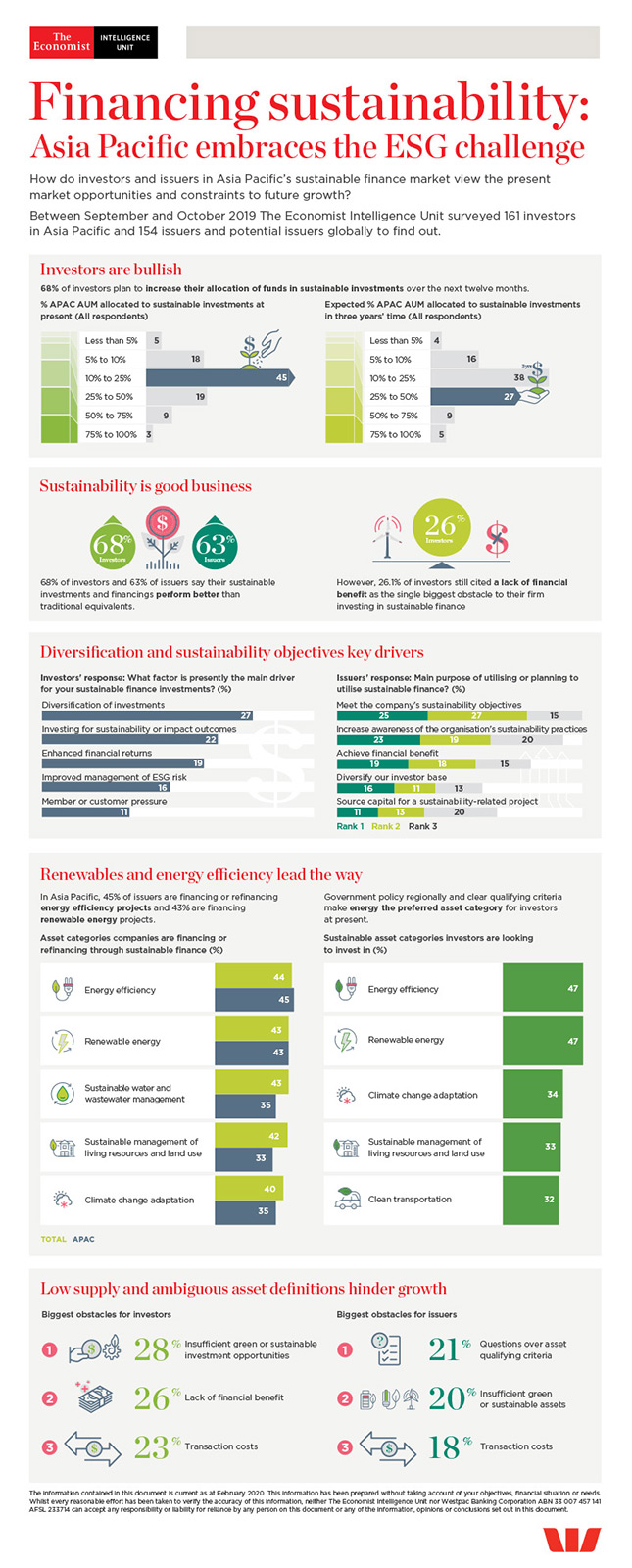
Financing sustainability: Asia Pacific embraces the ESG challenge is an Economist Intelligence Unit report, sponsored by Westpac. It explores the drivers of sustainable finance growth in Asia Pacific as well as the factors constraining it. The analysis is based on two parallel surveys—one of investors and one of issuers—conducted in September and October 2019.
If the countries of Asia Pacific are to limit the negative environmental effects of continued economic growth, and companies in the region are to mitigate their potential climate risks and make a positive business contribution through improving the environment and meeting the UN's Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), large volumes of investment in sustainable projects and businesses need to be mobilised. A viable sustainable finance market is taking shape in the region to channel commercial investor funds, and both investors and issuers say they are achieving a financial benefit from their investment and financing activities. The market is still in the early stages of development, however, and must expand and mature to meet investor needs.
The chief constraint on sustainable finance growth in the region has been the limited supply of bankable sustainable projects. Our research suggests supply is increasing, but with investor demand continuing to grow apace, the gap will remain an obstacle in the short- to medium-term. Among the organisations in our issuer survey, only 7% have used sustainable finance instruments to fund projects. However, nearly nine in ten (87%) said they intend to do so in the next year, which should begin to bridge the gap between supply and demand.
Based on issuers’ stated intentions, investors will have a range of instruments to choose from, including green loans and bonds and sustainability loans and bonds. Large numbers of investors indicate that they intend to deploy a greater proportion of capital to these over the next three years.

Financing sustainability | Infographic
Financing sustainability: How do investors and issuers in APAC's sustainable finance market view the present market opportunities and constraints?
To learn more:
Download report | Watch video
Fintech in ASEAN
To better understand the opportunities and challenges in developing a fintech business in seven ASEAN markets, The Economist Intelligence Unit conducted wide-ranging desk research supplemented by seven in-depth interviews with executives in Australia and ASEAN.
Download report and watch video interview to learn more.
Financing sustainability: How do investors and issuers in APAC's sustainable finance market view the present market opportunities and constraints?
To learn more:
Related content

Financing sustainability: Asia Pacific embraces the ESG challenge
Financing sustainability: Asia Pacific embraces the ESG challenge is an Economist Intelligence Unit report, sponsored by Westpac. It explores the drivers of sustainable finance growth in Asia Pacific as well as the factors constraining it. The analysis is based on two parallel surveys—one of investors and one of issuers—conducted in September and October 2019.
If the countries of Asia Pacific are to limit the negative environmental effects of continued economic growth, and companies in the region are to mitigate their potential climate risks and make a positive business contribution through improving the environment and meeting the UN's Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), large volumes of investment in sustainable projects and businesses need to be mobilised. A viable sustainable finance market is taking shape in the region to channel commercial investor funds, and both investors and issuers say they are achieving a financial benefit from their investment and financing activities. The market is still in the early stages of development, however, and must expand and mature to meet investor needs.
The chief constraint on sustainable finance growth in the region has been the limited supply of bankable sustainable projects. Our research suggests supply is increasing, but with investor demand continuing to grow apace, the gap will remain an obstacle in the short- to medium-term. Among the organisations in our issuer survey, only 7% have used sustainable finance instruments to fund projects. However, nearly nine in ten (87%) said they intend to do so in the next year, which should begin to bridge the gap between supply and demand.
Based on issuers’ stated intentions, investors will have a range of instruments to choose from, including green loans and bonds and sustainability loans and bonds. Large numbers of investors indicate that they intend to deploy a greater proportion of capital to these over the next three years.

Financing sustainability | Insights video
What is driving the strong demand for financing sustainability in Asia Pacific? How can companies increase supply and start to see the benefits of sustainable finance in the next three years? We interviewed Richard Brandweiner, CEO of Pendal Australia, and Sophia Cheng, CIO of Cathay Financial Holdings and chair of Asia Investor Group on Climate Change, to find out.
To learn more: Download report | View infographic
Fintech in ASEAN
To better understand the opportunities and challenges in developing a fintech business in seven ASEAN markets, The Economist Intelligence Unit conducted wide-ranging desk research supplemented by seven in-depth interviews with executives in Australia and ASEAN.
Download report and watch video interview to learn more.
Social impact: what does it mean, and how should we measure it?
Related content

Resetting the agenda: How ESG is shaping our future
The Covid-19 pandemic has exposed a wealth of interconnections – between ecological and human wellbeing, between economic and environmental fragility, between social inequality and health outcomes, and more. The consequences of these connections are now filtering through, reshaping our society and economy.
In this setting, the need to integrate environmental, social and governance (ESG) factors when investing has become even more critical. Institutional investors must employ ESG not just to mitigate risks and identify opportunities, but to engage with companies to bring about the positive change needed to drive a sustainable economic recovery in the post-Covid world.
In order to understand how ESG could be both a new performance marker and a growth driver in this environment, as well as how institutional investors are using ESG to make investment decisions and to assess their own performance, The Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU), sponsored by UBS, surveyed 450 institutional investors working in asset and wealth management firms, corporate pension funds, endowment funds, family offices, government agencies, hedge funds, insurance companies, pension funds, sovereign wealth funds and reinsurers in North America, Europe and Asia-Pacific.
Download the report and infographic to learn more.

Charting the course for ocean sustainability in the Indian Ocean Rim
Charting the course for ocean sustainability in the Indian Ocean Rim is an Economist Intelligence Unit report, sponsored by Environment Agency Abu Dhabi and the Department of Economic Development Abu Dhabi, which highlights key ocean challenges facing the Indian Ocean Rim countries and showcases initiatives undertaken by governments and the private sector in the region to address these challenges.
Click here to view the report.

Fixing Asia's food system
The urgency for change in Asia's food system comes largely from the fact that Asian populations are growing, urbanising and changing food tastes too quickly for many of the regions’ food systems to cope with. Asian cities are dense and are expected to expand by 578m people by 2030. China, Indonesia and India will account for three quarters of these new urban dwellers.
To study what are the biggest challenges for change, The Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU) surveyed 400 business leaders in Asia’s food industry. According to the respondents, 90% are concerned about their local food system’s ability to meet food security needs, but only 32% feel their organisations have the ability to determine the success of their food systems. Within this gap is a shifting balance of responsibility between the public and private sectors, a tension that needs to and can be strategically addressed.
Green intelligence: Asia’s ESG investing, data integrity and technology
Related content

The China position: Gauging institutional investor confidence
The China position: Gauging institutional investor confidence is an Economist Intelligence Unit report, comissioned by Invesco. It analyses results from a survey of 411 institutional investor and asset owner organisations (approximately 200 in Europe, Middle East and Africa, 100 in North America, and 100 from Asia-Pacific). The key findings of the survey are as follow:
A majority (nine in ten) of our survey respondents claim some level of dedicated exposure to China. Investments are growing; about half of respondents with dedicated China exposure report their investments have “risen significantly” in the past 12 months. Equities are the most-cited way organisations invest in China. Over 60% of respondents with dedicated China exposure report both equities and fixed income onshore holdings. Respondents cited improvements to their own China expertise as the top driver for dedicated investment exposure. Nearly four in ten respondents say environmental, social and governance (ESG) factors play a role in all of their investment decisions; fewer than three in ten say ESG is particularly important for China investments. Chinese asset classes in our survey could see increased investment from foreign organisations over the next 12 months, with respondents highlighting technology, financial services and “new economy” sectors as most attractive. Risk assessments are largely even across asset classes, but on a regional split respondents in APAC are more concerned than counterparts in North America or EMEA. Respondents are mixed on the impact of US-China trade tensions, with similar numbers expecting a positive or negative effect. But a majority of respondents report that their organisations expect to increase exposure over the next 12 months, regardless of outlook. About three-quarters of survey respondents say China’s economy will improve over the next 12 months; about two-thirds say the same for global economic conditions.Our thanks are due to the following individuals for their time and insights:
Jimmy Chang, chief investment strategist, Rockefeller Capital Management Mark Delaney, deputy chief executive and chief investment officer, Australian Super Kevin Wade, chief investment officer, Superannuation Arrangements of the University of London (SAUL)Download the report for more insights.

China icebergs: Forces that could reshape the world
China icebergs: Forces that could reshape the world is an Economist Intelligence Unit report, sponsored by PineBridge Investments, that examines hidden strengths in the Chinese economy—“icebergs”—that existing and potential investors into the world’s second-largest economy should be watching.
The US may have held its position as the world’s largest economy since 1871, but in the 1820s the world’s economic powerhouse was China, at almost 20 times the size of US GDP. China’s decline began in the 19th century and lasted until the country’s economic reforms that began in 1979. Since then, China has rapidly re-emerged as a major economy.China’s boom has helped fuel global growth, but it has also raised the country’s debt levels and prompted questions about economic endurance and global impact. Trends may be visible on the surface, but, like an iceberg, bigger implications lie underneath. To get a better understanding, this report aims to go below headline numbers and explore the nation’s commercial strengths and potential weaknesses. Key takeaways include:
The economy is shifting, and consumers are the driving force. Liberalisation of the private sector is shifting China from a state-backed to a consumption-led economy, which could fully transition by 2030. Chinese technological advances are compounding. From mobile internet to fintech to artificial intelligence and flying cars, Chinese firms are innovating and advances are feeding into the local economy as well as going global. New growth centres are emerging—exponentially. China’s lower-tier cities are growing fast and catching up to the mega-cities in terms of technology, commerce and infrastructure.What does the emergence of middle-class, digital-savvy consumers, the improving mobility of work and the rapid urbanisation mean for China's economy? We talked to Mr. Chibo Tang from Gobi Partners.
A Whole New World: How technology is driving the evolution of intelligent b...
Across the Asia-Pacific region, governments and regulators are already implementing new strategies to digitise their economies and boost social inclusion. Faster payment networks are spreading, facilitating the adoption of mobile payments and the development of open banking. With mobile payment infrastructure and services already embedded in major economies, Asia-Pacific banks are looking to the next challenge. Digital technology regulations lag other regions but are under review (37% of respondents believe that emerging data regulation will have a major impact on the banking sector) as Asia looks to modernise, diversify and dilute its dependence on international trade.
The race is on
In markets where mobile payments have already taken root, banks and payment processors are battling tech companies on two fronts. They are working to retain their own retail card and current-account customers and attract new users to their apps and e-wallets. They also need to get and keep merchants on their side if they are to reap the economies of scale from a high-volume, low-margin sector.
Competition is intensifying between payment solutions based on application programming interfaces (APIs) and pre-loaded and credit card e-wallets. That may explain why survey respondents see an immediate need to master digital engagement and marketing (37% for 2020) to pull in users and merchants. They also need to be able to respond quickly when Alipay, WeChat Pay, Google and WhatsApp introduce new features (31% for 2020).
In India, app providers are already offering cashbacks, discount vouchers and other features to gain and retain market share. This may leave the smaller players vulnerable, particularly when all that is required to switch services is downloading an app. It is therefore likely that consolidation of this sector will follow. As Vijay Shekhar Sharma, founder and chief executive of Paytm, has pointed out, payments are merely the moat around other, more profitable services. The players with deep pockets will outlive their weaker competitors.
The Monetary Authority of Singapore was met with similar concerns that disruptors would leave the banks unprofitable when it first suggested the introduction of open banking. When the regulator pointed out that tech and fintech firms could already offer faster, simpler and cheaper transaction services, the banks agreed to collaborate on upgrading the banking system, providing all stakeholders operated within the same regulatory environment.
Singapore is set to follow Hong Kong with virtual bank licences; ride-hailing app giant Grab is likely to be among the first applicants. That may worry established banks, but the question remains whether the big tech providers have the capacity to tie up capital in establishing their own bank operations. It is also not clear if they really want to expose themselves to the reputational risks that service interruptions or bad service present if they are the sole provider of such services. Grab already offers loans through a Japanese bank and recently signed up with Citibank to offer branded credit cards.2 If either of those services fail to deliver to consumers, the banks, not Grab, face the wrath of consumers and regulatory authorities.
Yet all Asian regulators are acutely aware of how Alipay and WeChat Pay were able to create an effective duopoly in an unregulated market. Chinese authorities are now bringing in new laws to level the playing field. Other authorities want to lay down the rules first, before such corrective action needs to be taken. As a result, the Chinese payment giants may find new markets tougher to crack when they must operate under tighter licensing and data protection rules.
As Steve Weston, co-founder of Australia’s Volt Bank, says of the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority: “The regulators are focused on ensuring that all banks, including new entrants, are operating in a prudent manner.”
Sustainability: Technology-enabled
17107
Related content

Sustainability: Moving the conversation forward
How sustainability is understood by businesses and investors has changed dramatically since it was first considered within corporate social responsibility (CSR) in the 1960s. It has grown from being an annual report to shareholders of the actions taken in relation to a company’s broader social and ethical obligations to become an integral part of many companies’ business strategies. However, following the global adoption of the UN’s sustainable development goals (SDGs) and the Paris Agreement, the concept of sustainability is now more often associated with the integration of environmental, social and governance (ESG) factors. These ESG factors cover a wide spectrum of issues that traditionally may not be part of a company’s strategy or included within its financial analysis and reporting. This might include quantitative measures of how corporations respond to climate change, as well as the more qualitative social and governance factors such as workforce training, shareholder protection and board diversity, and how companies manage their supply chains.
There is no global agreement on corporate social or sustainability reporting requirements. Yet over 93% of the world’s largest 250 corporations do follow voluntary reporting standards such as those set out in the Global Reporting Initiative and report on their sustainability performance. At the regional level, the European Union (EU) does have unified sustainability reporting, enforced through Directive 2014/95/EU. However, much of the push behind the incorporation of sustainability into business operations is coming from the globalisation of supply chains, and mounting pressures from investors, asset owners, non-government organisations and the general public for companies to report on ESG risks. As a result, there are significant differences in how the US, the EU and Asia are developing frameworks, programmes and legislation to achieve the global shift to sustainability.
The funding gap
One area that has come to globally symbolise sustainability is the SDGs, developed by the UN and agreed by world leaders in 2015. They include environmental issues such as water, energy and climate change, along with social issues, such as education and health services. They also cover the private sector, with goals for employment and industry.
Achieving these goals by 2030 will be costly. Estimates range from $6trn per year upwards equal to the entire annual economic output of Italy, India and Canada combined.
Europe – money talks
In January this year, the European Commission (EC) laid out plans to cement sustainability into the European financial system. It suggested introducing a classification system of what is “sustainable” and measures to impose conditions on corporate reporting requirements and the duties asset managers had to investors. The use of an ESG lens in particular means that, from a financial perspective, it is easier for companies and investors to integrate sustainability into their investment decisions, because it is quantifiable.
Many of the EC’s suggestions are already being put in place. An accounting rules change will allow governments to keep certain energy transition projects off their national balance sheets. In doing so, the EC hopes to unlock plans that have been frozen for fear of increasing national deficits.
The mandates of Europe’s banking, markets and pension regulators are also being expanded to include sustainability alongside financial stability.
Central bankers are already on board. The governor of the Bank of England, Mark Carney, has said many times that climate change could be a source of financial risk and instability if left unchecked.
Likewise, De Nederlandsche Bank (the Dutch central bank) is looking at ways to factor environmental risk into lending, borrowing and insurance as sea levels rise.
And France, through Article 173, is already pressing ahead with measures to push companies and those who invest in them to assess and disclose the impact of their activities on the environment.
Further EU legislation should be agreed by 2019 to compel the financial industry to deliver the €180bn needed each year to hit Europe’s climate change targets.
China – sustainability an economic value-add
Rapid economic growth has left China facing some of the most severe environmental issues on the planet. They range from Beijing’s life-threatening smog to untreated sewage in the 80% of cities without formal treatment facilities. This rapid growth has also left it with significant social disruption as populations moved from rural to urban areas and new mega cities (those with populations over 10mn) have sprung up.
Whilst recognising the investment cost required, China views sustainability as an opportunity for its companies to develop innovative technologies that will allow the country to move up the value-added export chain. What is clear is that it wants a return on its environmental investments.
By focusing on research and development, China hopes to lead the world in environmental technology. The strategy is already paying dividends; China now accounts for a greater share of environmental patent applications than Europe or North America.
Both industry and China’s current-account balance are benefiting. From batteries to car manufacturing and solar power, China has already overtaken the US as the world’s leading environmental technology exporter. However, as noted by the Conference Board, China still has to contend with the social and economic pressures that have built up as China has developed. Failing to address these sustainability issues could have serious future cost, reputation and growth consequences for businesses in China.
US: The states and market rebel
President Donald Trump has made it very clear he is no fan of climate change initiatives. During his election campaign, he promised to bring US coalmines back to life. In office, he has promised to pull the USout of the Paris Agreement. In January 2018 he slapped 30% tariffs on imported solar panels. This has led US renewable energy companies to cancel or freeze investments of more than $2.5bn in large installation projects. This is more than double the about $1bn in new spending plans announced by firms building or expanding US solar panel factories to take advantage of the tax on imports.
But not everyone agrees with him. In June 2018 the US Senate rejected his plans for deep cuts to renewable energy research budgets and individual states are developing their own projects (see box) without the need for federal regulation.
Download Article PDF here

Resetting the agenda: How ESG is shaping our future
The Covid-19 pandemic has exposed a wealth of interconnections – between ecological and human wellbeing, between economic and environmental fragility, between social inequality and health outcomes, and more. The consequences of these connections are now filtering through, reshaping our society and economy.
In this setting, the need to integrate environmental, social and governance (ESG) factors when investing has become even more critical. Institutional investors must employ ESG not just to mitigate risks and identify opportunities, but to engage with companies to bring about the positive change needed to drive a sustainable economic recovery in the post-Covid world.
In order to understand how ESG could be both a new performance marker and a growth driver in this environment, as well as how institutional investors are using ESG to make investment decisions and to assess their own performance, The Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU), sponsored by UBS, surveyed 450 institutional investors working in asset and wealth management firms, corporate pension funds, endowment funds, family offices, government agencies, hedge funds, insurance companies, pension funds, sovereign wealth funds and reinsurers in North America, Europe and Asia-Pacific.
Download the report and infographic to learn more.

Charting the course for ocean sustainability in the Indian Ocean Rim
Charting the course for ocean sustainability in the Indian Ocean Rim is an Economist Intelligence Unit report, sponsored by Environment Agency Abu Dhabi and the Department of Economic Development Abu Dhabi, which highlights key ocean challenges facing the Indian Ocean Rim countries and showcases initiatives undertaken by governments and the private sector in the region to address these challenges.
Click here to view the report.
Sustainability: Moving the conversation forward
How sustainability is understood by businesses and investors has changed dramatically since it was first considered within corporate social responsibility (CSR) in the 1960s. It has grown from being an annual report to shareholders of the actions taken in relation to a company’s broader social and ethical obligations to become an integral part of many companies’ business strategies.
17102
Related content

Resetting the agenda: How ESG is shaping our future
The Covid-19 pandemic has exposed a wealth of interconnections – between ecological and human wellbeing, between economic and environmental fragility, between social inequality and health outcomes, and more. The consequences of these connections are now filtering through, reshaping our society and economy.
In this setting, the need to integrate environmental, social and governance (ESG) factors when investing has become even more critical. Institutional investors must employ ESG not just to mitigate risks and identify opportunities, but to engage with companies to bring about the positive change needed to drive a sustainable economic recovery in the post-Covid world.
In order to understand how ESG could be both a new performance marker and a growth driver in this environment, as well as how institutional investors are using ESG to make investment decisions and to assess their own performance, The Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU), sponsored by UBS, surveyed 450 institutional investors working in asset and wealth management firms, corporate pension funds, endowment funds, family offices, government agencies, hedge funds, insurance companies, pension funds, sovereign wealth funds and reinsurers in North America, Europe and Asia-Pacific.
Download the report and infographic to learn more.

Charting the course for ocean sustainability in the Indian Ocean Rim
Charting the course for ocean sustainability in the Indian Ocean Rim is an Economist Intelligence Unit report, sponsored by Environment Agency Abu Dhabi and the Department of Economic Development Abu Dhabi, which highlights key ocean challenges facing the Indian Ocean Rim countries and showcases initiatives undertaken by governments and the private sector in the region to address these challenges.
Click here to view the report.

Fixing Asia's food system
The urgency for change in Asia's food system comes largely from the fact that Asian populations are growing, urbanising and changing food tastes too quickly for many of the regions’ food systems to cope with. Asian cities are dense and are expected to expand by 578m people by 2030. China, Indonesia and India will account for three quarters of these new urban dwellers.
To study what are the biggest challenges for change, The Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU) surveyed 400 business leaders in Asia’s food industry. According to the respondents, 90% are concerned about their local food system’s ability to meet food security needs, but only 32% feel their organisations have the ability to determine the success of their food systems. Within this gap is a shifting balance of responsibility between the public and private sectors, a tension that needs to and can be strategically addressed.
Can automation and AI support the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals?
Automation, artificial intelligence (AI) and other innovations of the Fourth Industrial Revolution are set to drastically change society, promising extraordinary benefits including increased productivity and improved public services. However, these innovations are also fuelling growing techno-anxiety. Unemployment is the most commonly discussed threat, with labour organisations, governments and economists all voicing concern that human workers may be displaced at an unprecedented scale and speed, which could worsen inequality, undermine social cohesion and increase poverty.
17079
Related content

Accelerating urban intelligence: People, business and the cities of tomorro...
About the research
Accelerating urban intelligence: People, business and the cities of tomorrow is an Economist Intelligence Unit report, sponsored by Nutanix. It explores expectations of citizens and businesses for smart-city development in some of the world’s major urban centres. The analysis is based on two parallel surveys conducted in 19 cities: one of 6,746 residents and another of 969 business executives. The cities included are Amsterdam, Copenhagen, Dubai, Frankfurt, Hong Kong, Johannesburg, London, Los Angeles, Mumbai, New York, Paris, Riyadh, San Francisco, São Paulo, Singapore, Stockholm, Sydney, Tokyo and Zurich.
Respondents to the citizen survey were evenly balanced by age (roughly one-third in each of the 18-38, 39-54 and 55 years and older age groups) and gender. A majority (56%) had household incomes above the median level in their city, with 44% below it. Respondents to the business survey were mainly senior executives (65% at C-suite or director level) working in a range of different functions. They work in large, midsize and small firms in over a dozen industries. See the report appendix for full survey results and demographics.
Additional insights were obtained from indepth interviews with city officials, smart-city experts at NGOs and other institutions, and business executives. We would like to thank the following individuals for their time and insights.
Pascual Berrone, academic co-director, Cities in Motion, and professor, strategic management, IESE Business School (Barcelona) Lawrence Boya, director, Smart City Programme, city of Johannesburg Amanda Daflos, chief innovation officer, city of Los Angeles Linda Gerull, chief information officer, city of San Francisco Praveen Pardeshi, municipal commissioner, Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation (Mumbai) • Brian Roberts, policy analyst, city of San Francisco Sameer Sharma, global general manager, Internet of Things (IoT), Intel • Marius Sylvestersen, programme director, Copenhagen Solutions Lab Tan Kok Yam, deputy secretary of the Smart Nation and Digital Government, Prime Minister’s Office, SingaporeThe report was written by Denis McCauley and edited by Michael Gold.

Talent for innovation
Talent for innovation: Getting noticed in a global market incorporates case studies of the 34 companies selected as Technology Pioneers in biotechnology/health, energy/environmental technology, and information technology.
Leonardo Da Vinci unquestionably had it in the 15th century; so did Thomas Edison in the 19th century. But today, "talent for innovation" means something rather different. Innovation is no longer the work of one individual toiling in a workshop. In today's globalised, interconnected world, innovation is the work of teams, often based in particular innovation hotspots, and often collaborating with partners, suppliers and customers both nearby and in other countries.
Innovation has become a global activity as it has become easier for ideas and talented people to move from one country to another. This has both quickened the pace of technological development and presented many new opportunities, as creative individuals have become increasingly prized and there has been greater recognition of new sources of talent, beyond the traditional innovation hotspots of the developed world.
The result is a global exchange of ideas, and a global market for innovation talent. Along with growth in international trade and foreign direct investment, the mobility of talent is one of the hallmarks of modern globalisation. Talented innovators are regarded by companies, universities and governments as a vital resource, as precious as oil or water. They are sought after for the simple reason that innovation in products and services is generally agreed to be a large component, if not the largest component, in driving economic growth. It should be noted that "innovation" in this context does not simply mean the development of new, cutting-edge technologies by researchers.
It also includes the creative ways in which other people then refine, repackage and combine those technologies and bring them to market. Indeed, in his recent book, "The Venturesome Economy", Amar Bhidé, professor of business at Columbia University, argues that such "orchestration" of innovation can actually be more important in driving economic activity than pure research. "In a world where breakthrough ideas easily cross national borders, the origin of ideas is inconsequential," he writes. Ideas cross borders not just in the form of research papers, e-mails and web pages, but also inside the heads of talented people. This movement of talent is not simply driven by financial incentives. Individuals may also be motivated by a desire for greater academic freedom, better access to research facilities and funding, or the opportunity to work with key researchers in a particular field.
Countries that can attract talented individuals can benefit from more rapid economic growth, closer collaboration with the countries where those individuals originated, and the likelihood that immigrant entrepreneurs will set up new companies and create jobs. Mobility of talent helps to link companies to sources of foreign innovation and research expertise, to the benefit of both. Workers who emigrate to another country may bring valuable knowledge of their home markets with them, which can subsequently help companies in the destination country to enter those markets more easily. Analysis of scientific journals suggests that international co-authorship is increasing, and there is some evidence thatcollaborative work has a greater impact than work carried out in one country. Skilled individuals also act as repositories of knowledge, training the next generation and passing on their accumulated wisdom.
But the picture is complicated by a number of concerns. In developed countries which have historically depended to a large extent on foreign talent (such as the United States), there is anxiety that it is becoming increasingly difficult to attract talent as new opportunities arise elsewhere. Compared with the situation a decade ago, Indian software engineers, for example, may be more inclined to set up a company in India, rather than moving to America to work for a software company there. In developed countries that have not historically relied on foreign talent (such as Germany), meanwhile, the ageing of the population as the birth rate falls and life expectancy increases means there is a need to widen the supply of talent, as skilled workers leave the workforce and young people show less interest than they used to in technical subjects. And in developing countries, where there is a huge supply of new talent (hundreds of thousands of engineers graduate from Indian and Chinese universities every year), the worry is that these graduates have a broad technical grounding but may lack the specialised skills demanded by particular industries.
Other shifts are also under way. The increasing sophistication of emerging economies (notably India and China) is overturning the old model of "create in the West, customise for the East". Indian and Chinese companies are now globally competitive in many industries. And although the mobility of talent is increasing, workers who move to another country are less likely to stay for the long-term, and are more likely to return to their country of origin. The number of Chinese students studying abroad increased from 125,000 in 2002 to 134,000 in 2006, for example, but the proportion who stayed in the country where they studied after graduating fell from 85% to 69% over the same period, according to figures from the OECD (see page 10).
What is clear is that the emergence of a global market for talent means gifted innovators are more likely to be able to succeed, and new and unexpected opportunities are being exploited, as this year's Technology Pioneers demonstrate. They highlight three important aspects of the global market for talent: the benefits of mobility, the significant role of diasporas, and the importance of network effects in catalysing innovation.
Brain drain, or gain?
Perhaps the most familiar aspect of the debate about flows of talent is the widely expressed concern about the "brain drain" from countries that supply talented workers. If a country educates workers at the taxpayers' expense, does it not have a claim on their talent? There are also worries that the loss of skilled workers can hamper institutional development and drive up the cost of technical services. But such concerns must be weighed against the benefits of greater mobility.
There are not always opportunities for skilled individuals in their country of birth. The prospect of emigration can encourage the development of skills by individuals who may not in fact decide to emigrate. Workers who emigrate may send remittances back to their families at home, which can be a significant source of income and can help to alleviate poverty. And skilled workers may return to their home countries after a period working abroad, further stimulating knowledge transfer and improving the prospects for domestic growth, since they will maintain contacts with researchers overseas. As a result, argues a recent report from the OECD, it makes more sense to talk of a complex process of "brain circulation" rather than a one-way "brain drain". The movement of talent is not simply a zero-sum gain in which sending countries lose, and receiving countries benefit. Greater availability and mobility of talent opens up new possibilities and can benefit everyone.
Consider, for example, BioMedica Diagnostics of Windsor, Nova Scotia. The company makes medical diagnostic systems, some of them battery-operated, that can be used to provide health care in remote regions to people who would otherwise lack access to it. It was founded by Abdullah Kirumira, a Ugandan biochemist who moved to Canada in 1990 and became a professor at Acadia University. There he developed a rapid test for HIV in conjunction with one of his students, Hermes Chan (a native of Hong Kong who had moved to Canada to study). According to the United States Centers for Disease Control, around one-third of people tested for HIV do not return to get the result when it takes days or weeks to determine. Dr Kirumira and Dr Chan developed a new test that provides the result in three minutes, so that a diagnosis can be made on the spot. Dr Kirumira is a prolific inventor who went on to found several companies, and has been described as "the pioneer of Nova Scotia's biotechnology sector".
Today BioMedica makes a range of diagnostic products that are portable, affordable and robust, making them ideally suited for use in developing countries. They allow people to be rapidly screened for a range of conditions, including HIV, hepatitis, malaria, rubella, typhoid and cholera. The firm's customers include the World Health Organisation. Providing such tests to patients in the developing world is a personal mission of Dr Kirumira's, but it also makes sound business sense: the market for invitro diagnostics in the developing world is growing by over 25% a year, the company notes, compared with growth of only 5% a year in developed nations.
Moving to Canada gave Dr Kirumira research opportunities and access to venture funding that were not available in Uganda. His innovations now provide an affordable way for hospitals in his native continent of Africa to perform vital tests. A similar example is provided by mPedigree, a start-up that has developed a mobile-phone-based system that allows people to verify the authenticity of medicines. Counterfeit drugs are widespread in the developing world: they are estimated to account for 10-25% of all drugs sold, and over 80% in some countries. The World Health Organisation estimates that a fake vaccine for meningitis, distributed in Niger in 1995, killed over 2,500 people. mPedigree was established by Bright Simons, a Ghanaian social entrepreneur, in conjunction with Ashifi Gogo, a fellow Ghanaian. The two were more than just acquaintances having met at Secondary School. There are many high-tech authentication systems available in the developed world for drug packaging, involving radio-frequency identification (RFID) chips, DNA tags, and so forth.
The mPedigree system developed my Mr Gogo, an engineering student, is much cheaper and simpler and only requires the use of a mobile phone — an item that is now spreading more quickly in Africa than in any other region of the world. Once the drugs have been purchased, a panel on the label is scratched off to reveal a special code. The patient then sends this code, by text message, to a particular number. The code is looked up in a database and a message is sent back specifying whether the drugs are genuine. The system is free to use because the drug companies cover the cost of the text messages. It was launched in Ghana in 2007, and mPedigree's founders hope to extend it to all 48 sub-Saharan African countries within a decade, and to other parts of in the developing world.
The effort is being supported by Ghana's Food and Drug Board, and by local telecoms operators and drug manufacturers. Mr Gogo has now been admitted into a special progamme at Dartmouth College in the United States that develops entrepreneurial skills, in addition to technical skills, in engineers. Like Dr Kirumira, he is benefiting from opportunities that did not exist in his home country, and his country is benefiting too. This case of mPedigree shows that it is wrong to assume that the movement of talent is one-way (from poor to rich countries) and permanent. As it has become easier to travel and communications technology has improved, skilled workers have become more likely to spend brief spells in other countries that provide opportunities, rather than emigrating permanently.
And many entrepreneurs and innovators shuttle between two or more places — between Tel Aviv and Silicon Valley, for example, or Silicon Valley and Hsinchu in Taiwan — in a pattern of "circular" migration, in which it is no longer meaningful to distinguish between "sending" and "receiving" countries.
The benefits of a diaspora
Migration (whether temporary, permanent or circular) to a foreign country can be facilitated by the existence of a diaspora, since it can be easier to adjust to a new culture when you are surrounded by compatriots who have already done so. Some observers worry that diasporas make migration too easy, in the sense that they may encourage a larger number of talented individuals to leave their home country than would otherwise be the case, to the detriment of that country.
But as with the broader debate about migration, this turns out to be only part of the story. Diasporas can have a powerful positive effect in promoting innovation and benefiting the home country. Large American technology firms, for example, have set up research centres in India in part because they have been impressed by the calibre of the migrant Indian engineers they have employed in America. Diasporas also provide a channel for knowledge and skills to pass back to the home country.
James Nakagawa, a Canadian of Japanese origin and the founder of Mobile Healthcare, is a case in point. A third-generation immigrant, he grew up in Canada but decided in 1994 to move to Japan, where he worked for a number of technology firms and set up his own financial-services consultancy. In 2000 he had the idea that led him to found Mobile Healthcare, when a friend was diagnosed with diabetes and lamented that he found it difficult to determine which foods to eat, and which to avoid.
The rapid spread of advanced mobile phones in Japan, a world leader in mobile telecoms, prompted Mr Nakagawa to devise Lifewatcher, Mobile Healthcare's main product. It is a "disease selfmanagement system" used in conjunction with a doctor, based around a secure online database that can be accessed via a mobile phone. Patients record what medicines they are taking and what food they are eating, taking a picture of each meal. A database of common foodstuffs, including menu items from restaurants and fast-food chains, helps users work out what they can safely eat. Patients can also call up their medical records to follow the progress of key health indicators, such as blood sugar, blood pressure, cholesterol levels and calorie intake.
All of this information can also be accessed online by the patient's doctor or nutritionist. The system allows people with diabetes or obesity (both of which are rapidly becoming more prevalent in Japan and elsewhere) to take an active role in managing their conditions. Mr Nakagawa did three months of research in the United States and Canada while developing Lifewatcher, which was created with support from Apple (which helped with hardware and software), the Japanese Red Cross and Japan's Ministry of Health and Welfare (which provided full access to its nutritional database).
Japanese patients who are enrolled in the system have 70% of the cost covered by their health insurance. Mr Nakagawa is now working to introduce Lifewatcher in the United States and Canada, where obesity and diabetes are also becoming more widespread — along advanced mobile phones of the kind once only found in Japan. Mr Nakagawa's ability to move freely between Japanese and North American cultures, combining the telecoms expertise of the former with the entrepreneurial approach of the latter, has resulted in a system that can benefit both.
The story of Calvin Chin, the Chinese-American founder of Qifang, is similar. Mr Chin was born and educated in America, and worked in the financial services and technology industries for several years before moving to China. Expatriate Chinese who return to the country, enticed by opportunities in its fast-growing economy, are known as "returning turtles". Qifang is a "peer to peer" (P2P) lending site that enables students to borrow money to finance their education from other users of the site. P2P lending has been pioneered in other countries by sites such as Zopa and Prosper in other countries.
Such sites require would-be borrowers to provide a range of personal details about themselves to reassure lenders, and perform credit checks on them. Borrowers pay above-market rates, which is what attracts lenders. Qifang adds several twists to this formula. It is concentrating solely on student loans, which means that regulators are more likely to look favourably on the company's unusual business model. It allows payments to be made directly to educational institutions, to make sure the money goes to the right place. Qifang also requires borrowers to give their parents' names when taking out a loan, which increases the social pressure on them not to default, since that would cause the family to lose face.
Mr Chin has thus tuned an existing business model to take account of the cultural and regulatory environment in China, where P2P lending could be particularly attractive, given the relatively undeveloped state of China's financial-services market. In a sense, Qifang is just an updated, online version of the community group-lending schemes that are commonly used to finance education in China. The company's motto is that "everyone should be able to get an education, no matter their financial means".
Just as Mr Chin is trying to use knowledge acquired in the developed world to help people in his mother country of China, Sachin Duggal hopes his company, Nivio, will do something similar for people in India. Mr Duggal was born in Britain and is of Indian extraction. He worked in financial services, including a stint as a technologist at Deutsche Bank, before setting up Nivio, which essentially provides a PC desktop, personalised with a user's software and documents, that can be accessed from any web browser.
This approach makes it possible to centralise the management of PCs in a large company, and is already popular in the business world. But Mr Duggal hopes that it will also make computing more accessible to people who find the prospect of owning and managing their own PCs (and dealing with spam and viruses) too daunting, or simply cannot afford a PC at all. Nivio's software was developed in India, where Mr Duggal teamed up with Iqbal Gandham, the founder of Net4India, one of India's first internet service providers. Mr Duggal believes that the "virtual webtop" model could have great potential in extending access to computers to rural parts of India, and thus spreading the opportunities associated with the country's high-tech boom. A survey of the bosses of Indian software firms clearly shows how diasporas can promote innovation.
It found that those bosses who had lived abroad and returned to India made far more use of diaspora links upon their return than entrepreneurs who had never lived abroad, which gave them access to capital and skills in other countries. Diasporas can, in other words, help to ensure that "brain drain" does indeed turn into "brain gain", provided the government of the country in question puts appropriate policies in place to facilitate the movement of people, technology and capital.
Making the connection
Multinational companies can also play an important role in providing new opportunities for talented individuals, and facilitating the transfer of skills. In recent years many technology companies have set up large operations in India, for example, in order to benefit from the availability of talented engineers and the services provided by local companies. Is this simply exploitation of low-paid workers by Western companies?
The example of JiGrahak Mobility Solutions, a start-up based in Bangalore, illustrates why it is not. The company was founded by Sourabh Jain, an engineering graduate from the Delhi Institute of Technology. After completing his studies he went to work for the Indian research arm of Lucent Technologies, an American telecoms-equipment firm. This gave him a solid grounding in mobile-phone technology, which subsequently enabled him to set up JiGrahak, a company that provides a mobile-commerce service called Ngpay.
In India, where many people first experience the internet on a mobile phone, rather than a PC, and where mobile phones are far more widespread than PCs, there is much potential for phone-based shopping and payment services. Ngpay lets users buy tickets, pay bills and transfer money using their handsets. Such is its popularity that with months of its launch in 2008, Ngpay accounted for 4% of ticket sales at Fame, an Indian cinema chain.
The role of large companies in nurturing talented individuals, who then leave to set up their own companies, is widely understood in Silicon Valley. Start-ups are often founded by alumni from Sun, HP, Oracle and other big names. Rather than worrying that they could be raising their own future competitors, large companies understand that the resulting dynamic, innovative environment benefits everyone, as large firms spawn, compete with and acquire smaller ones.
As large firms establish outposts in developing countries, such catalysis of innovation is becoming more widespread. Companies with large numbers of employees and former employees spread around the world can function rather like a corporate diaspora, in short, providing another form of network along which skills and technology can diffuse. The network that has had the greatest impact on spreading ideas, promoting innovation and allowing potential partners to find out about each other's research is, of course, the internet. As access to the internet becomes more widespread, it can allow developing countries to link up more closely with developed countries, as the rise of India's software industry illustrates. But it can also promote links between developing countries.
The Cows to Kilowatts Partnership, based in Nigeria, provides an unusual example. It was founded by Joseph Adelagan, a Nigerian engineer, who was concerned about the impact on local rivers of effluent from the Bodija Market abattoir in Ibadan. As well as the polluting the water supply of several nearby villages, the effluent carried animal diseases that could be passed to humans. Dr Adelagan proposed setting up an effluent-treatment plant.
He discovered, however, that although treating the effluent would reduce water pollution, the process would produce carbon-dioxide and methane emissions that contribute to climate change. So he began to look for ways to capture these gases and make use of them. Researching the subject online, he found that a research institution in Thailand, the Centre for Waste Utilisation and Management at King Mongkut University of Technology Thonburi, had developed anaerobic reactors that could transform agro-industrial waste into biogas. He made contact with the Thai researchers, and together they developed a version of the technology
suitable for use in Nigeria that turns the abattoir waste into clean household cooking gas and organic fertiliser, thus reducing the need for expensive chemical fertiliser. The same approach could be applied across Africa, Dr Adelagan believes. The Cows to Kilowatts project illustrates the global nature of modern innovation, facilitated by the free movement of both ideas and people. Thanks to the internet, people in one part of the world can easily make contact with people trying to solve similar problems elsewhere.
Lessons learned
What policies should governments adopt in order to develop and attract innovation talent, encourage its movement and benefit from its circulation? At the most basic level, investment in education is vital. Perhaps surprisingly, however, Amar Bhidé of Columbia University suggests that promoting innovation does not mean pushing as many students as possible into technical subjects.
Although researchers and technologists provide the raw material for innovation, he points out, a crucial role in orchestrating innovation is also played by entrepreneurs who may not have a technical background. So it is important to promote a mixture of skills. A strong education system also has the potential to attract skilled foreign students, academics and researchers, and gives foreign companies an incentive to establish nearby research and development operations.
Many countries already offer research grants, scholarships and tax benefits to attract talented immigrants. In many cases immigration procedures are "fast tracked" for individuals working in science and technology. But there is still scope to remove barriers to the mobility of talent. Mobility of skilled workers increasingly involves short stays, rather than permanent moves, but this is not yet widely reflected in immigration policy. Removing barriers to short-term stays can increase "brain circulation" and promote diaspora links.
Another problem for many skilled workers is that their qualifications are not always recognised in other countries. Greater harmonisation of standards for qualifications is one way to tackle this problem; some countries also have formal systems to evaluate foreign qualifications and determine their local equivalents. Countries must also provide an open and flexible business environment to ensure that promising innovations can be brought to market. If market access or financial backing are not available, after all, today's global-trotting innovators increasingly have the option of going elsewhere.
The most important point is that the global competition for talent is not a zero-sum game in which some countries win, and others lose. As the Technology Pioneers described here demonstrate, the nature of innovation, and the global movement of talent and ideas, is far more complicated that the simplistic notion of a "talent war" between developed and developing nations would suggest. Innovation is a global activity, and granting the greatest possible freedom to innovators can help to ensure that the ideas they generate will benefit the greatest possible number of people.

Integrated Transformation: How rising customer expectations are turning com...
Modern customers have it good. Spoilt for choice and convenience, today’s empowered consumers have come to expect more from the businesses they interact with. This doesn’t just apply to their wanting a quality product at a fair price, but also tailored goods, swift and effective customer service across different channels, and a connected experience across their online shopping and in-store experience, with easy access to information they need when they want it.
Meeting these expectations is a significant challenge for organisations. For many, it requires restructuring long-standing operating models, re-engineering business processes and adopting a fundamental shift in mindset to put customer experience at the heart of business decision- making. Download our report to learn more.
Chỉ số Thương mại Bền vững Hinrich Foundation
Chỉ số Thương mại Bền vững - Hinrich Foundation 2018 là một chỉ số được xây dựng bởi Economist Intelligence Unit và là một nghiên cứu quy chuẩn được ủy thác bởi Hinrich Foundation. Đây là ấn bản thứ hai của nghiên cứu, được xuất bản lần đầu năm 2016. Đây là ấn bản thứ hai của nghiên cứu, chỉ số đầu tiên được xuất bản vào năm 2016. Báo cáo trình bày các kết quả chính của chỉ số và mô hình kèm theo.
Related content

The Hinrich Foundation Sustainable Trade Index 2018
Yet the enthusiasm in Asia for trade does not appear to have waned. This broad societal consensus behind international trade has enabled Asian countries to continue broadening and deepening existing trading relationships, for example, by quickly hammering out a deal for the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) in early 2018 following the US’s withdrawal from its predecessor in 2017.
Asia, then, finds itself in the unique position of helping lead and sustain the global economy’s commitment to free and fair trade. It is in this context that the need for sustainability in trade is ever more crucial.
The Hinrich Foundation Sustainable Trade Index was created for the purpose of stimulating meaningful discussion of the full range of considerations that policymakers, business executives, and civil society leaders must take into account when managing and advancing international trade.
The index was commissioned by the Hinrich Foundation, a non-profit organisation focused on promoting sustainable trade. This, the second edition of the study, seeks to measure the capacity of 20 economies—19 in Asia along with the US—to participate in the international trading system in a manner that supports the long-term domestic and global goals of economic growth, environmental protection, and strengthened social capital. The index’s key findings include:
Countries in Asia, especially the richer ones, have broadly regressed in terms of trade sustainability. Hong Kong is developed Asia’s bright spot, recording a slight increase in its score and topping the 2018 index. Several middle-income countries perform admirably, led by Sri Lanka. For the economic pillar, countries generally performed well in terms of growing their labour forces as well as their per-head GDPs. For the social pillar, sharp drops for some countries in certain social pillar indicators contribute to an overall decline. For the environmental pillar, with deteriorating environmental sustainability in many rich countries, China, Laos and Pakistan are the only countries to record increases in scores. Sustainability is an ever more important determinant of FDI and vendor selection in choosing supply-chain partners. Companies are improving the sustainability of their supply chains by restructuring and broadening relationships with competitors and vendors.
The Global Illicit Trade Environment Index 2018
To measure how nations are addressing the issue of illicit trade, the Transnational Alliance to Combat Illicit Trade (TRACIT) has commissioned The Economist Intelligence Unit to produce the Global Illicit Trade Environment Index, which evaluates 84 economies around the world on their structural capability to protect against illicit trade. The global index expands upon an Asia-specific version originally created by The Economist Intelligence Unit in 2016 to score 17 economies in Asia.
View the Interactive Index >> Download workbook

Breaking Barriers: Agricultural trade between GCC and Latin America
The GCC-LAC agricultural trading relationship has thus far been dominated by the GCC’s reliance on food imports, specifically meat, sugar, and cereals. Over the past two years, however, there has been a notable decline in the share of sugar imported from LAC, and 2017 saw the biggest importers in the GCC—Saudi Arabia and the UAE—impose a ban on Brazilian meat.
Market players on both sides of the aisle are keen to grow the relationship further, but there are hurdles to overcome. In this report, we explore in greater depth the challenges that agricultural exporters and importers in LAC and the GCC face. We consider both tariff and non-tariff barriers and assess key facets of the trading relationship including transport links, customs and certification, market information, and trade finance.
Key findings of the report:
GCC will need to continue to build partnerships to ensure a secure supply of food. Concerns over food security have meant that the GCC countries are exploring ways to produce more food locally. However, given the region’s climate and geology, food imports will remain an important component of the food supply. Strengthening partnerships with key partners such as those in LAC, from which it sourced 9% of its total agricultural imports in 2016, will be vital to food security in the region.
There is a wider range of products that the LAC countries can offer the GCC beyond meat, sugar and cereals. Providing more direct air links and driving efficiencies in shipping can reduce the time and cost of transporting food products. This will, in turn, create opportunities for LAC exporters to supply agricultural goods with a shorter shelf life or those that are currently too expensive to transport. Exporters cite examples such as berries and avocados.
The GCC can engage small and medium-sized producers that dominate the LAC agricultural sector by offering better trade financing options and connectivity. More direct air and sea links can reduce the cost of transporting food products, making it viable for smaller players to participate in agricultural trade. The existing trade financing options make it prohibitive for small and medium-sized players too. Exporters in LAC suggest that local governments and private companies in the GCC can offer distribution services with immediate payments to smaller suppliers at a discount.
Blockchain technology is poised to address key challenges market players face in agricultural trade. Through a combination of smart contracts and data captured through devices, blockchain technology can help to reduce paperwork, processing times and human error in import and export processes. It can improve transparency, as stakeholders can receive information on the state of goods and status of shipments in real time. Finally, it can help with food safety and quality management—monitoring humidity and temperature, for instance, along the supply chain can help to pinpoint batches that may be contaminated, minimising the need for a blanket ban on a product.

