Inforaphic Mobile Image
Jesse is a managing editor for Economist Impact based in Asia, with a focus on healthcare.
Based in Hong Kong, Jesse has been working in Asia for over 10 years. Prior to the Economist Impact, he held roles in medical education, scientific publications and medical communications, working in multinational biopharmaceutical companies with a focus in vaccines and biologic medicines. Jesse has extensive experience researching and collating medical information and working with healthcare professionals and patient organisations to develop insight-driven communications programmes.
Jesse holds a BSc in Anatomy and Physiology from the University of Leeds. His editorial interests include the policy response to emerging public health issues and patient advocacy in infectious diseases.

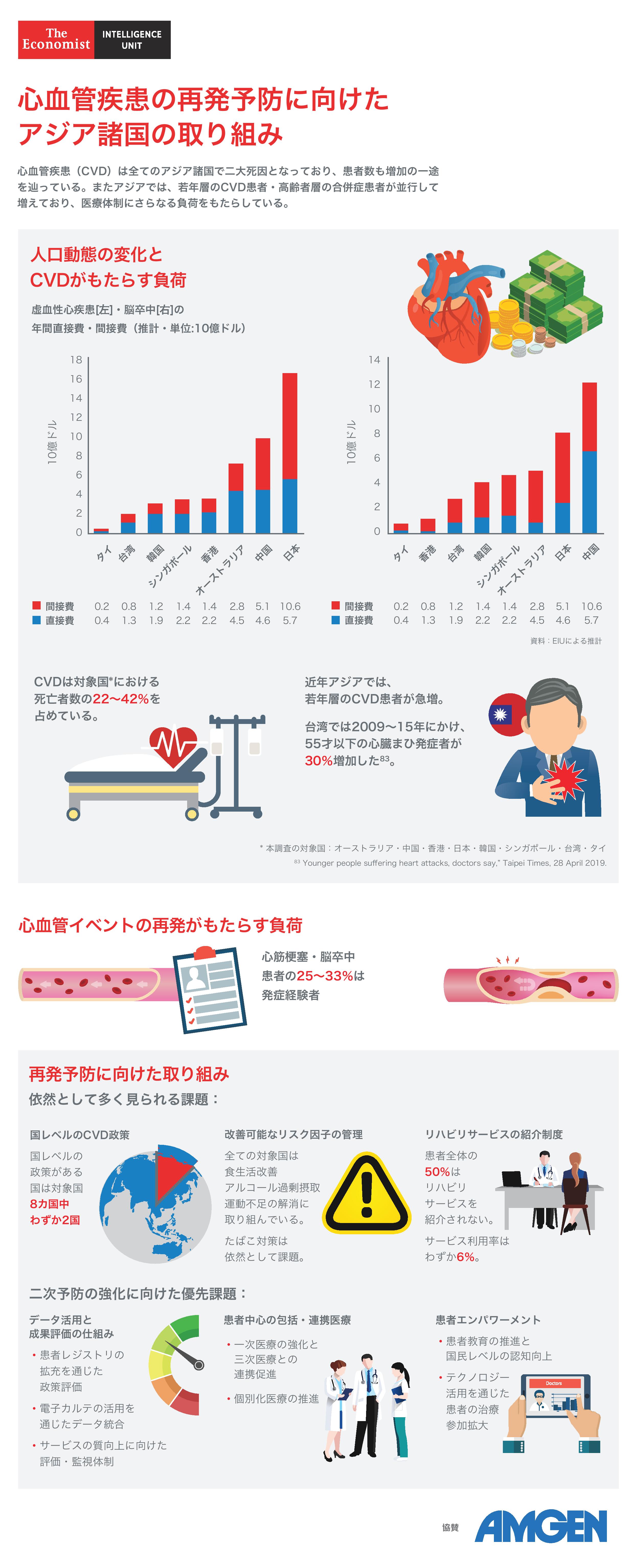
아시아 태평양 지역의 심혈관 질환(CVD)부담은 국가별로 상이하나 모두 상당하다.CVD는 지역 전반에서 사망 원인 1위 또는2위를 차지하고 있으며, 유병률도 계속높아지고 있다. 또한 CVD를 경험하는 젊은환자와 여러 동반 이환을 가진 고령화 인구두 집단 모두의 증가라는 지역 내 인구통계적변화로 인해 각국의 보건의료체계에 부하가걸리고 있다.
CVD 관련 문제 해결에 관한 진척은 1차예방 분야에 초점이 맞춰져 이루어져왔으며, CVD의 연령표준화 발생률은감소하기 시작했다. 그러나 여전히 허용할수 없는 높은 수준의 심장마비 및 뇌졸중재발률과 그에 따른 경제적 및 인적 비용이존재해 이러한 진척을 저해하고 있다. 첫심장마비 또는 뇌졸중 생존자가 더많아짐에 따라 2차 사건 관련 부담이증가할 가능성이 높다. 이는 긴급한 주의를요구하는 상황인 동시에, 해당 환자 집단의관리와 결과를 개선할 수 있는 탁월하고현실적인 기회이기도 하다.
본 이코노미스트 인텔리전스 유닛분석에서는 아시아 태평양 지역8개국(호주, 중국, 홍콩, 일본, 싱가포르,한국, 대만, 태국)의 2차 심혈관 사건관리에 대한 정책적 대응을 살펴본다. 본 연구의 주요 결과는 다음을 포함한다. 관련 정책은 확실히 존재하나, 정책이상당히 포괄적인 국가도 있고 그렇지 않은국가도 있다. 조절 가능한 위험인자에 대한 정책을 법률과실천에 성공적으로 반영했는지 여부와 그로인한 영향은 아직 확인되지 않았다. 정부 감사가 결여되어 있다. 통합 관리의 핵심 요소인 1차 의료 체계가발전하고 있다. 재활 서비스가 존재하나 보장 범위가제한적이며, 업체들은 환자 유치와 유지에어려움을 겪고 있다. 필요한 목표는 환자 중심의 통합적이고조정된 관리 환자 권한부여는 성공의 핵심 데이터 극대화 및 진척도 측정
亚太地区心血管疾病的负担因国家/地区而异,但无论任何国家/地区都负担沉重。总体来说,心血管疾病在该地区是造成死亡的首要或次要原因,其患病率也在不断增长。除此以外,该地区人口结构的变化——患心血管疾病的年轻人增加,同时患有多种合并症的老龄人口也呈增长趋势——令医疗系统越来越不堪重负。
应对心血管疾病相关问题的进展主要集中于一级预防领域,同时心血管疾病年龄标准化患病率也正在降低。然而心脏病和卒中复发的几率长期居高不下,令人难以接受,而与之相关的经济和人力成本亦威胁着已经取得的进步。由于越来越多的患者能在心脏病或卒中首次发病时幸存,复发事件所带来的负担很可能会更加沉重。这一状况需要紧急的关注,但同时也带来了一个非常有可能实现的机遇——改善该患者群体所接受的医疗护理及其效果。
本次由经济学人智库(The Economist Intelligence Unit/The EIU)所做的分析探究了亚太地区在管理心血管疾病复发事件上的政策响应措施,研究主要聚焦于以下八个经济体:澳大利亚、中国大陆、中国香港、中国台湾、日本、新加坡、韩国以及泰国。
本研究主要发现包括:
虽然确实存在心血管疾病政策,但有些政策比其他政策更为全面。 将可改变的风险因素有关的政策落实到立法和行动层面的措施是否成功,以及对其影响的评估方法都有待界定。 缺乏政府审计。 初级医疗系统作为综合医疗的关键组成部分,正在不断升级。 康护服务存在但是覆盖范围有限,同时这些项目很难召集和留住患者。 必需确定以患者为中心的综合、协调医疗护理目标. 患者赋权是成功的制胜法宝. 最大程度推进数据和衡量进度.

Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) account for around one quarter of deaths in Australia.1 The Economist Intelligence Unit estimates that the annual direct and indirect costs of CVD in Australia totals US$12.3bn.2 There are numerous modifiable risk factors for CVD, but the most important include hypertension (high blood pressure), high cholesterol, tobacco use, diabetes and obesity.3 While much of the recent focus has been on primary prevention through lifestyle modification, those highrisk patients with existing CVD—such as peripheral artery disease or a previous heart attack or stroke—require particular attention to avoid further morbidity and mortality.
The improved use of data and digital health tools has the potential to enable more coordinated and patient-centred models of care. The Digital Health CRC takes this further in saying “research and innovation in digital health offers Australia significant economic and business development opportunities, as well as great promise for the better health of our community”.4
On 27 May 2020, The Economist Intelligence Unit—supported by the Australian Cardiovascular Alliance (ACvA) and Digital Health CRC and with sponsorship from Amgen—convened a virtual roundtable discussion with 25 representatives from across the Australian cardiovascular healthcare landscape.
Co-hosted by the Economist Intelligence Unit with Dr Gemma Figtree, president of ACvA and professor in medicine at University of Sydney & Royal North Shore Hospital, and Dr Tim Shaw, director of research and workforce capacity at Digital Health CRC, the roundtable aimed to identify barriers, challenges and opportunities to improve outcomes for highrisk CVD patients by improving the use of data and digital technologies.
1 Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Cardiovascular disease. In: Welfare AIoHa, editor. Canberra 2019. 2 Economist Intelligence Unit. “The cost of silence: Cardiovascular disease in Asia”, 2019 3 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “Know your risk for heart diseases”. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/risk_factors.htm (Accessed Jun 2020). 4 Digital Health CRC. “About us”. Available from: https://www.digitalhealthcrc.com/about-us/ (Accesed Jun 2020).
Enjoy in-depth insights and expert analysis - subscribe to our Perspectives newsletter, delivered every week
The Economist Group is a global organisation and operates a strict privacy policy around the world. Please see our privacy policy here
