China, South Korea and the US Federal Reserve have started quarantining or disinfecting banknotes. It is well-known that currency in circulation can serve as a vehicle for transmitting pathogens, though the potency of pathogens transmitted via cash remains unclear. The human influenza virus, for example, can remain alive and infectious for more than two weeks on banknotes. Although it’s not known whether the exchange of currency infected with influenza can dramatically increase its spread, responses from the US, Korean and Chinese governments raise concerns.
It’s possible that these governments are simply taking extreme precautionary measures. It’s also possible that physical currency can indeed be a significant transmission medium for highly infectious diseases such as covid-19. A local branch of the People's Bank of China in Guangzhou has even opted to destroy banknotes that have been in circulation in high-risk settings such as hospitals or wet-markets.
These measures reflect earlier governmental responses to infectious disease. A late 1940s report on Egypt’s cholera epidemic highlighted the viability of cholera pathogens on banknotes. Throughout history people have responded to sickness in a similar way by washing or fumigating banknotes, yet we still have limited understanding of how physical currencies might transmit new pathogens.
There’s no doubt that covid-19 will accelerate the pre-existing trend towards digital payments in Asia, and China in particular. In late October 2019, Chinese President Xi Jinping endorsed blockchain—a digital ledger technology on which digital currencies can be transacted—as “an important breakthrough for independent innovation of core technologies”. He added that the People’s Bank of China intended to replace cash with a government-issued digital currency. The Chinese government actively promotes its internet banking infrastructure, whereas Western nations rarely use a top-down approach to governance.
In China, where digital payments are already prevalent, covid-19 could be a significant driver for the total elimination of cash. In 2018, nearly 73% of Chinese internet users made online payments (up from 18% in 2008). According to a recent survey by Deutsche Bank, this increase is partly driven by young people who are typically more open to adopting new technologies. China and Southeast Asian countries have much larger young populations than Europe and the US.
Western countries have tended to move at a slower pace towards digital payments than, for example, China. Part of the reason for this lies, according to Deutsche Bank, in different payment cultures of countries. A third of the people in OECD countries consider cash to be their favourite payment method, and more than half believe cash will always be around. Citizens in many European countries (notably Germany) and those in the US have a marked preference for cash.
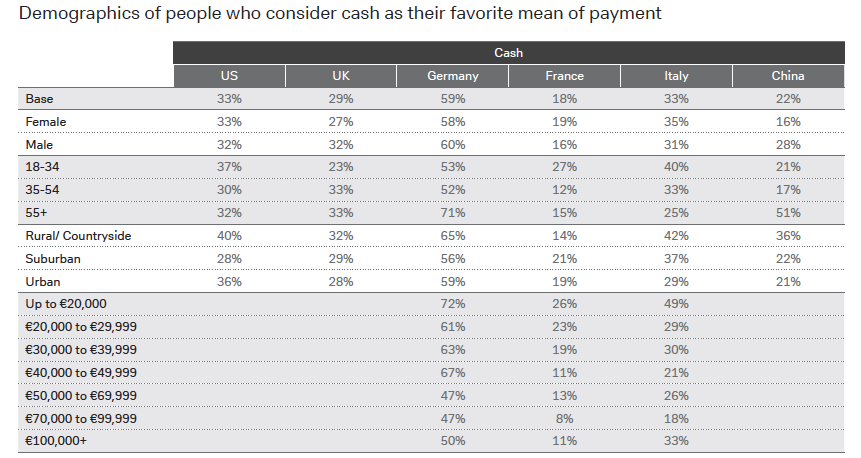 Source: Deutsche Bank, The Future of Payments.
Source: Deutsche Bank, The Future of Payments.
But even in Western countries that share similar payment cultures we can observe variation in digital preparedness. In terms of homegrown fintech champions that could benefit most from a digital payments transition, Europe’s are much smaller in size than large US counterparts such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, and PayPal—to name a few. Beyond that, many of Europe’s leading digital payment service companies are controlled or backed by US and Chinese companies (eg Swedish financial technology company IZettle was recently acquired by PayPal and Germany’s mobile N26 bank is backed by China’s Tencent).
Nonetheless, European countries are determined to be at the forefront of digital currencies. Central banks such as the Bank of England, the European Central Bank, the Swiss National Bank and the Swedish Riksbank have started to assess the feasibility of digital central bank currencies. These would perform all the functions of banknotes and coins and could then be used by households and businesses to make both payments and savings. The transition will not be easy. Digital central bank currencies require infrastructure that can record in-person and online transactions, which means that governments will need private sector co-operation.
Under “normal” conditions it would take a long time to change culturally ingrained habits and institutional legacies related to long and well-established payments systems. Jodie Kelley—CEO of the US Electronic Transactions Association—said in a recent interview that “people default to what’s familiar, unless there’s something to jolt you out of it”. She continued that “contactless payments have come up as a new option for consumers who are much more conscious of what they touch”.
The covid-19 pandemic could move the world more rapidly towards digital payments. In France, the Louvre museum in Paris recently banned cash due to covid-19 fears. The museum did this even though its policy clashes with the Bank of France's requirement that all businesses accept cash.
It is too early to conclude what the changes might look like in each cultural, demographic, and institutional context, but we can be sure that covid-19 is already reinforcing existing trends towards increased digitisation of payments.
Dr Marion Laboure and Sachin Silva are the co-authors of this blog. Marion Laboure is a macro strategist at Deutsche Bank and Sachin Silva is a doctoral candidate and fellow at Harvard University specialising in global health and economics.
The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of The Economist Group or any of its affiliates. The Economist Group cannot accept any responsibility or liability for reliance by any person on this article or any of the information, opinions or conclusions set out in the article.